IR Spectroscopy: Definition, Instrumentation, Working and Applications
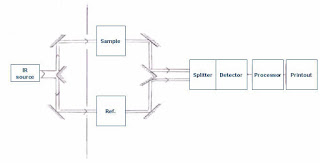
What is IR Spectroscopy? Infrared spectroscopy is absorption spectroscopy that deals with the recording of the absorption of the electromagnetic radiations of the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The IR region ranges from 700-1000 nm. This technique is widely used for the detecting of functional groups, characterization of proteins, analysis of various liquids, and identification of molecules and their composition. Instrumentation of IR spectroscopy 1. Radiation source The radiation source should emit IR electromagnetic radiations which are steady, intense, and extended over the desired wavelength. That's why radiation sources like Nernst glower, globar source, incandescent lamp, and mercury arc lamp. 2. Monochromator It helps to select desired frequencies of IR radiations because our sample will only absorb some specific frequencies of IR radiations. Prism and grating are the most commonly used monochromators. 3. Sample cells and sampling IR spectroscopy is ...