Polycarbonates: Structure, Preparation, Properties and Application
What are Polycarbonates?
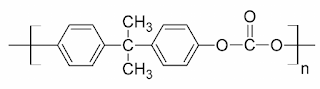
Polycarbonate (PC) are high-performance tough thermoplastic polymers that have organic functional groups linked together by carbonate groups (-O-(C=O)-O-).
Polycarbonates have high impact resistance and are obtained by condensation of diethyl carbonate or carbonyl chloride and bisphenol-A. It is widely used for bullet-proof windows and safety or crash helmets. Lexan is the most common example of Polycarbonates.
Structure of Polycarbonate
Preparation of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is produced by condensation polymerization between bisphenol A and either Carbonyl chloride or diphenyl carbonate.
(a) Preparation of Polycarbonate by condensation polymerization between bisphenol-A and Carbonyl Chloride
The polymer is usually formed by the reaction of bisphenol-A and carbonyl chloride in a basic solution where polymerization takes place at the interface between the aqueous and organic layer with the help of a catalyst can amine.
(b) Preparation of Polycarbonate by condensation polymerization between bisphenol-A and diphenyl Carbonate
Polycarbonate can also be made by condensation polymerization of bisphenol-A and diphenyl carbonate to eliminate the use of carbonyl chloride (Phosgene) which is an extremely poisonous gas.
Properties of Polycarbonate
1. Polycarbonate has high strength making it resistant to impact and fracture. The polymer can maintain its toughness up to 140 ℃ and down to -20 ℃.
2. Polycarbonate is an extremely clear plastic that can transmit over 90% light as good as glass.
3. Polycarbonate has a refractive index of 1.584 and offers excellent optical properties.
4. Polycarbonate exhibits good chemical resistance against diluted acids, aliphatic hydrocarbons, and alcohols.
5. Polycarbonates are thermally stable up to 135 ℃ offering good heat resistance. Their heat resistance can also be improved by adding flame retardants with impacting material properties.
Applications of Polycarbonates
1. Polycarbonates are used in electrical appliances such as refrigerates, air conditioners, coffee machines, food mixers, etc.
2. Polycarbonates are also used in bulletproof windows, shelters, skylights acting as the best alternative to glass.
3. Polycarbonate has great medical applications where it is used in surgical instruments, drug delivery systems, hemodialysis membranes, blood filters, etc.
4. Because of its heat resistance and shatter resistance, it is used in applications for direct contact with food and beverages. Food storage containers mode from polycarbonate are re-usable, help to preserve freshness, protect food from contamination, and can be conveniently used in a refrigerator or microwave.