Polycarbonates: Structure, Preparation, Properties and Application
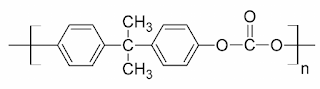
What are Polycarbonates? Polycarbonate (PC) are high-performance tough thermoplastic polymers that have organic functional groups linked together by carbonate groups (-O-(C=O)-O-). Polycarbonates have high impact resistance and are obtained by condensation of diethyl carbonate or carbonyl chloride and bisphenol-A. It is widely used for bullet-proof windows and safety or crash helmets. Lexan is the most common example of Polycarbonates. Structure of Polycarbonate Preparation of Polycarbonate Polycarbonate is produced by condensation polymerization between bisphenol A and either Carbonyl chloride or diphenyl carbonate. (a) Preparation of Polycarbonate by condensation polymerization between bisphenol-A and Carbonyl Chloride The polymer is usually formed by the reaction of bisphenol-A and carbonyl chloride in a basic solution where polymerization takes place at the interface between the aqueous and organic layer with the help of a catalyst can amine. (b) Preparation of Polycarbonat...